Iron supported on bioinspired green silica for water remediation†
Abstract
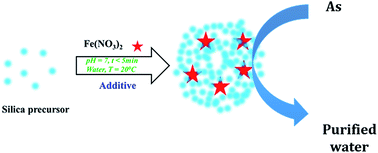
Iron has been used previously in water decontamination, either unsupported or supported on clays, polymers, carbons or ceramics such as silica. However, the reported synthesis procedures are tedious, lengthy (involving various steps), and either utilise or produce toxic chemicals. Herein, the use of a simple, rapid, bio-inspired green synthesis method is reported to prepare, for the first time, a family of iron supported on green nanosilica materials (Fe@GN) to create new technological solutions for water remediation. In particular, Fe@GN were employed for the removal of arsenate ions as a model for potentially toxic elements in aqueous solution. Several characterization techniques were used to study the physical, structural and chemical properties of the new Fe@GN. When evaluated as an adsorption platform for the removal of arsenate ions, Fe@GN exhibited high adsorption capacity (69 mg of As per g of Fe@GN) with superior kinetics (reaching ∼35 mg As per g sorbent per hr) – threefold higher than the highest removal rates reported to date. Moreover, a method was developed to regenerate the Fe@GN allowing for a full recovery and reuse of the adsorbent in subsequent extractions; strongly highlighting the potential technological benefits of these new green materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...