Modification of shape memory polymer foams using tungsten, aluminum oxide, and silicon dioxide nanoparticles
Abstract
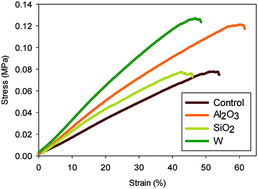
Shape memory polymer (SMP) foams were synthesized with three different nanoparticles (tungsten, silicon dioxide, and aluminum oxide) for embolization of cerebral aneurysms. Ultra-low density SMP foams have previously been utilized for aneurysm occlusion, resulting in a rapid, stable thrombus. However, the small cross section of foam struts can potentially lead to fracture and particulate generation, which would be a serious adverse event for an embolic device. The goal of this study was to improve the mechanical properties of the system by physically incorporating fillers into the SMP matrix. Thermal and mechanical characterization suggested minimal changes in thermal transition of the SMP nanocomposites and improved mechanical strength and toughness for systems with low filler content. Actuation profiles of the three polymer systems were tuned with filler type and content, resulting in faster SMP foam actuation for nanocomposites containing higher filler content. Additionally, thermal stability of the SMP nanocomposites improved with increasing filler concentration, and particulate count remained well below accepted standard limits for all systems. Extraction studies demonstrated little release of silicon dioxide and aluminum oxide from the bulk over 16 days. Tungsten release increased over the 16 day examination period, with a maximum measured concentration of approximately 2.87 μg mL−1. The SMP nanocomposites developed through this research have the potential for use in medical devices due to their tailorable mechanical properties, thermal resistivity, and actuation profiles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...