Investigation of the in situ generation of oxide-free copper nanoparticles using pulsed-laser ablation of bulk copper in aqueous solutions of DNA bases†
Abstract
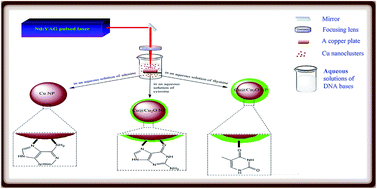
The pulsed-laser ablation (PLA) method was used as a facile and green approach to prepare oxide-free copper nanoparticles (Cu NPs), and was performed by laser ablation of a copper target in aqueous solutions of DNA bases (adenine, cytosine, and thymine). The structural analyses reveal that the in situ adsorption of the cytosine and thymine molecules on the surface of Cu NPs, although improving the stability of the colloids, cannot prevent the interaction of Cu NPs with the dissolved oxygen. However, the nanoparticles obtained in the aqueous solution of adenine are free from an oxide layer, indicating the high stabilizing effect of adenine molecules on the copper nanoparticles. FT-IR spectroscopy was used to study the mode of interaction of the DNA bases with the Cu NPs. Our results show that the participation of the nitrogen atoms of the DNA bases in the coordination to the Cu surface has a significant effect on the stabilization of the Cu NPs. In the case of adenine, the FT-IR spectra reveal that the excellent stabilizing effect originates from the ability of adenine to protect the laser-generated Cu NPs through its –NH2 group and imidazole nitrogen atoms. Thymine has no such nitrogen atoms and the NH2 group of cytosine cannot significantly participate in the coordination to the Cu surface. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the preparation of oxide-free copper nanoparticles by the laser ablation of bulk copper in aqueous solutions containing small neutral biomolecules. The synthesized Cu NPs/adenine shows effective antibacterial activity against Gram-negative Escherichia coli and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...