Improved electromembrane microextraction efficiency of chloramphenicol in dairy products: the cooperation of reduced graphene oxide and a cationic surfactant
Abstract
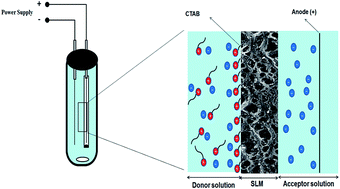
A novel method of electromembrane extraction combined with HPLC analysis was applied for preconcentration–determination of chloramphenicol (CAP) residues in dairy products. It is shown that the presence of the cationic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) in the sample solution, and reduced graphene oxide (RGO) in the solvent membrane, results in the enhancement of the anionic analyte extraction into the acceptor phase. In fact, the addition of CTAB leads the accumulation of the analyte at the sample solution/supported liquid membrane (SLM) interface, and thus amelioration of the analyte transfer rate to the acceptor phase. The effect of RGO on this process comes from its efficient sorbent characteristic which augments the overall analyte partition coefficient into the SLM. The main parameters that affect the extraction efficiency were examined and optimized. Under the optimized conditions, the proposed method provided acceptable linearity (0.04–250 ng g−1), satisfactory repeatability and reproducibility (CV% < 5.5), low LODs (0.012–0.021 ng g−1) with high preconcentration factors (195–255) in the different samples. Finally, the proposed method was successfully applied to the evaluation of CAP residues in dairy products.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...