Ciprofloxacin wastewater treated by UVA photocatalysis: contribution of irradiated TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on the final toxicity as assessed by Vibrio fischeri†
Abstract
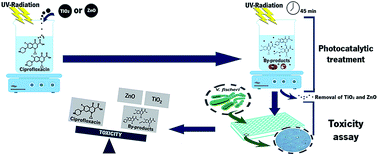
Photocatalysis has become an attractive process to treat wastewater since it allows a rapid and efficient degradation of micropollutants in water. A solution of ciprofloxacin (CIP) was photocatalytically treated by ultraviolet A light (UVA) and titanium dioxide (TiO2) or zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Toxicity of CIP and of the treated CIP solutions, as well as the toxicity of TiO2 and ZnO irradiated nanoparticles, was evaluated towards Vibrio fischeri. The lowest concentration of CIP tested, 10 μg L−1, leads to 50% of luminescence inhibition. Regarding irradiated nanoparticles, ZnO presented higher bacteria luminescence inhibition than TiO2, 97 and 38%, respectively. Due to high toxicity of ZnO, it was only possible to evaluate the CIP solution treated by UVA/TiO2. Initially, the toxicity decreased with the time of the process, but after 15 min the toxicity increased significantly (55%) and after 45 min of treatment, was 70%. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis proved that the initial decrease of toxicity was caused by CIP adsorption on catalyst surface, which latter increased due to the generation of by-products and toxicity contribution of soluble nanoparticles. Ten by-products were identified by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and the mechanism of CIP photocatalytic degradation was proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...