Ex vivo electric power generation in human blood using an enzymatic fuel cell in a vein replica†
Abstract
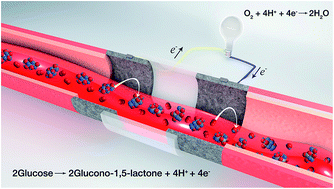
Here we report an enzymatic fuel cell in a vein replica that generates sustained electricity, enough to power an e-ink display, in an authentic human blood stream. We also detail a simple and safe approach for fuel cell evaluation under homeostatic conditions. Our results demonstrate proof-of-principle operation of a biocompatible and safe biodevice that could be implanted in superficial human veins, which we anticipate to be a starting point for more sophisticated investigations of personal sources of electricity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...