Rice protein radicals: growth and stability under microwave treatment
Abstract
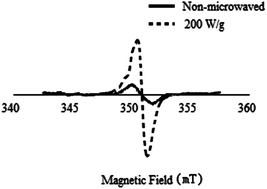
The change of protein structure in a microwave field is often presumed to be caused by free radicals. This study addressed whether protein in a microwave field would generate free radicals, and which factors affect the formation and stability of the free radicals. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy was used to investigate the signal of radicals in microwave-treated rice protein. The results revealed carbon-centred radicals in the treated rice protein samples. Spectral analysis of the rice protein revealed the presence of radicals not only in the thermally treated samples, but also in native samples of rice protein. The growth of radicals was strongly influenced by the water activity. Under microwave radiation, the intensity of the protein radicals increased as the water activity decreased and the microwave power increased. The intensity and growth rate increased with the radiation time. During storage time, the signal of the radicals dropped to 85% of the original value within 1 h. However, the radical signal gradually increased to its original level by the fifth day. Then, the EPR signal continued to decline at a slow pace until the intensity decreased to 75% of the original level. Based on the heating characteristics of oven heating, a temperature-controlled program during microwave heating was designed to compare the intensity of radicals after the two heating methods. The results indicated that microwave treatment induced much stronger radical signals, and the increase of the radical growth rate under microwave heating mostly occurred at 80–100 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...