High power plasma as an efficient tool for polymethylpentene cytocompatibility enhancement
Abstract
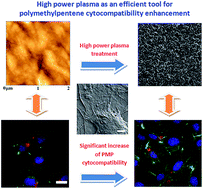
High power plasma was successfully used as an efficient and inexpensive tool for polymethylpentene (PMP) cytocompatibility enhancement. Proper surface roughness and morphology as well as the surface chemistry of a material are essential factors for successful utilization of a substrate intended for tissue engineering applications. Plasma treatment is an inexpensive, simple and highly effective method for optimization of surface properties, as a result of which enhancement of cell adhesion, growth and migration occurs. Oxygen and argon plasma treatments were applied to activate the PMP surface. The research was focused on the investigation of the changed properties. The AFM and FIB-SEM study demonstrated that plasma treatments of PMP induced structured surfaces which depended on the applied plasma setting. Measurement of the goniometry, and chemical changes (functional groups by FTIR, element concentration by XPS and RBS/ERDA) was included. Experiments on treated substrates with mouse fibroblasts (NIH 3T3) have shown a significant increase in cell adhesion and proliferation on treated PMP substrates when compared to the untreated polymer. Similarly, cell morphology and adhesion sites were carefully examined using fluorescence and scanning electron microscopy; results of both techniques confirmed the suitability of treated PMP samples for cell cultivation. This study demonstrates how to easily improve cytocompatibility of a very inert and resistant polymer for tissue engineering applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...