Ion-exchange bonded H2Ti3O7 nanosheets-based magnetic nanocomposite for dye removal via adsorption and its regeneration via synergistic activation of persulfate†
Abstract
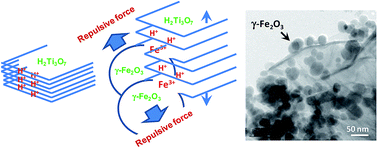
Magnetic nanocomposites (HTNSF) consisting of hydrogen titanate (H2Ti3O7) nanosheets (HTNS) and maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles with varying weight-fraction (5–25 wt%) of the latter have been successfully synthesized by simple mechanical mixing of precursors in an aqueous solution having neutral solution-pH. A new model has been proposed to explain the typical attachment of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles to the edges of HTNS via an ion-exchange bond formation. The dye-adsorption properties of HTNSF magnetic nanocomposites have been investigated using the cationic methylene blue (MB) dye as a target pollutant. The new model satisfactorily explains a strong dependence of positive deviation (relative to the variation governed by the law-of-mixture) observed in the variation of dye-adsorption capacity on the similar variation observed in the pore volume of HTNSF magnetic nanocomposite as a function of weight-fraction of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. The maximum MB adsorption capacity of 76 mg g−1 is exhibited by HTNSF-10 sample which is higher than that (67 mg g−1) of HTNS sample. The MB adsorption on the surface of HTNSF magnetic nanocomposite follows the pseudo-second-order kinetics and Langmuir and Dubinin–Kaganer–Radushkevich (DKR) isotherm models. The variation in the regression correlation coefficient (〈r2〉) values as a function of initial MB concentration strongly supports the Azizian analysis. The HTNSF-5 magnetic nanocomposite which contains the lowest weight-fraction (5 wt%) of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles shows the effective magnetic separation from the aqueous solution in 5 min. The reuse of HTNSF-5 magnetic nanocomposite has been successfully achieved through its regeneration via activation of persulfate (S2O82−) in an aqueous solution involving the synergy effect in between thermal activation and that by the constituents of HTNSF-5 magnetic nanocomposite.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...