A sulfonated Schiff base dimethyltin(iv) coordination polymer: synthesis, characterization and application as a catalyst for ultrasound- or microwave-assisted Baeyer–Villiger oxidation under solvent-free conditions†
Abstract
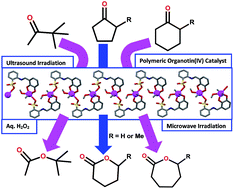
The synthesis and crystal structure of the new dimethyltin(IV) compound [SnMe2(HL)(CH3OH)]n·(0.5nCH3OH) (1) derived from the Schiff base 2-[(2,3-dihydroxyphenyl)methylideneamino]benzenesulfonic acid (H3L) are described. Despite having six potentially donating centres (one imine nitrogen, two phenoxo and three sulfonate oxygen atoms), the monoprotonated dianionic ligand (HL2−) behaves as an O,O,O-tridentate chelator. Single crystal X-ray diffraction revealed that 1 is a 1D coordination polymer with every tin(IV) ion bound to two methyl groups, a methanol molecule, two Ophenoxo and one μ-Osulfonate atom from HL2−. The coordination polymer 1 was applied as a heterogeneous catalyst for the Baeyer–Villiger oxidation of ketones to esters or lactones, using aqueous hydrogen peroxide as oxidant, under ultrasound (US) or microwave (MW) irradiation and solvent- and additive-free conditions. Overall conversions up to 76/82, 98/93, 93/89, 91/94, 83/90, 68/62 and 81/87% under US/MW irradiations were obtained with 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone, cyclopentanone, 2-methylcyclopentanone, cyclohexanone, 3-methylcyclohexanone, benzophenone and acetophenone, respectively. The catalyst can be recycled up to five cycles without losing appreciable activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...