Dendronized PLGA nanoparticles with anionic carbosilane dendrons as antiviral agents against HIV infection†
Abstract
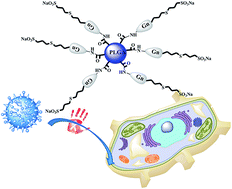
The development of novel strategies to prevent HIV-1 infection is of outstanding relevance. PLGA nanoparticles have become some of the most used nanosized materials for biomedical applications. Polyanionic carbosilane dendrimers and dendrons have shown potent and broad-spectrum anti-HIV-1 activity. Therefore, PLGA nanoparticles functionalized with carbosilane anionic dendrons through a carbodiimide-mediated reaction have been prepared with the aim of them becoming novel antiviral agents against HIV infection. The biocompatibility of the new dendronized nanoparticles has been explored in PBMC and HEC-1A cells. Both inhibition experiments showed differences between dendronized nanoparticles, free dendrons and PLGA nanoparticles. The results obtained with the dendronized nanoparticles indicate that these systems are powerful anti-HIV agents, compared to dendrons or dendrimers alone or PLGA NPs, suggesting an enhancement of their interaction with viral or cell receptors. The topology and size of these new systems could be responsible for the higher activity observed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...