Redox activity of lignite and its accelerating effects on the chemical reduction of azo dye by sulfide†
Abstract
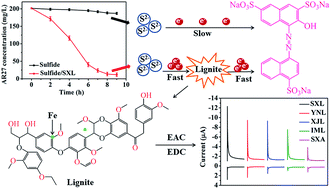
The search and development of an efficient and cost-effective redox mediator is essential for rapid decolorization of azo dye wastewater. Here, for the first time the electron shuttling activity of different lignite samples was assessed and utilized to promote azo dye reduction by sulfide. Mediated electrochemical reduction and oxidation analysis indicated that the lignite samples possessed a higher electron accepting capacity but negligible electron donating capacity. And the promotion effects of lignite samples seemed to be determined by their electron accepting capacities. It was found that the lignite-mediated decolorization performance increased with the increase of sulfide concentration (0–3.0 mM), lignite dosage (0–300 mg L−1) and salinity (0–6% NaCl). Over 80% decolorization could be kept in eight successive rounds of operation, revealing the persistent acceleration effects of lignite. Measurement and comparison of individual reaction rates not only further confirmed the redox mediator activity of lignite, but also identified the first step, i.e., reduction of lignite by sulfide to be the rate-limiting step of mediated azo dye decolorization. Additionally, redox transformation was observed with lignite's oxygenated moieties and iron components, which were believed to contribute to lignite's redox mediator activity. Based on the findings of this study, redox-active lignite could be used to enhance the treatment of wastewater containing azo dyes and other oxidative pollutants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...