Influence of the Al content on the in vitro bioactivity and biocompatibility of PVD Ti1−xAlxN coatings for orthopaedic applications†
Abstract
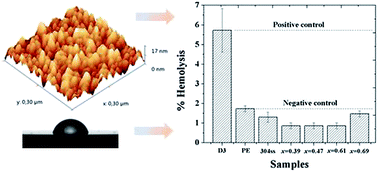
Titanium aluminium nitride (Ti1−xAlxN) coatings are utilized in industrial applications because of their excellent tribological and anticorrosive properties. Recently these coatings have been proposed for biomedical applications. In this paper, the biocompatibility and bioactivity of Ti1−xAlxN coatings, having various aluminium contents, x, deposited on AISI 304SS stainless steel, have been studied. Coatings were synthesized by magnetron co-sputtering by varying the power applied to the aluminium target. Morphology, chemical composition and microstructure were studied by SEM, AFM, XPS and XRD. Biocompatibility was assessed by measuring haemolytic and cytotoxic characteristics. Haemolysis was measured following the ASTM F756 norm. The in vitro cytotoxicity was assessed with human osteoblasts by means of the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay. Bioactivity was measured by soaking the samples in a simulated body fluid (SBF) and analysing the surfaces by XPS, XRD and SEM. It was found that all the Ti1−xAlxN coatings exhibited good biocompatibility and bioactivity, precipitating hydroxyapatite and monetite. The aluminium content in the Ti1−xAlxN coatings increases the quantity of calcium and phosphates groups precipitated in the beginning of the process, but it was also observed an influence of the roughness in the quantity of apatite precipitated after 1 month of immersion in SBF. The coating with x = 0.69 exhibited the higher bioactivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...