n-Type phosphorus-doped nanocrystalline diamond: electrochemical and in situ Raman spectroelectrochemical study†
Abstract
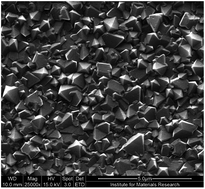
Electrochemical and in situ Raman spectroelectrochemical characterization of n-type phosphorus-doped nanocrystalline diamond (P-NCD) is carried out. The P-NCD films are grown by microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition and doped with phosphorus at a concentration of 10 000 ppm in the gas phase. Micro-Raman spectroscopy determines the film quality (presence of graphitic or amorphous phases). All electrochemical measurements are performed in aqueous 0.5 M H2SO4 electrolyte solution. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) confirms the n-type conduction of a P-NCD electrode and from the Mott–Schottky plot the donor concentration (ND) of 1.8 × 1018 cm−3 is determined. The in situ Raman spectroelectrochemistry is performed in the potential range from −1.5 to 1.5 V vs. Ag/AgCl using two laser excitations (633 nm and 488 nm). In the case of the as-prepared P-NCD film, the Raman modes belonging to non-diamond (sp2) impurities change their intensities during applied potentials. The intensity of such Raman peaks increases at cathodic potentials, while at anodic potentials they disappear. On the other hand, the intensity and position of the sp3 diamond peak (1334 cm−1) exhibit no spectroelectrochemical changes and the same holds for the photoluminescence peak (at 1.68 eV) assigned to Si-impurities. After several cyclic voltammetry (CV) scans, the electrochemical potential window of a P-NCD electrode increases. This is due to the “electrochemical burning” of impurities at large anodic potentials, which is also confirmed by in situ Raman spectroelectrochemistry. Angle-resolved XPS confirms partial electrochemical oxidation of P-NCD in thin surface layers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...