Surface functionalization of chitosan isolated from shrimp shells, using salicylaldehyde ionic liquids in exploration for novel economic and ecofriendly antibiofoulants†
Abstract
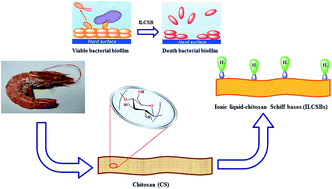
Since the use of organotin as antifouling additives was prohibited in 2003, many researchers have endeavored to design and develop novel economic environment-friendly marine antifouling additives. This work reports the successful functionalization of biopolymeric chitosan, isolated from shrimp shells, with salicylidene ionic liquid (IL-Sal) brushes, (ILCSB1–6). These designed architectures were structurally and morphologically characterized. Marine biofouling-inducing bacterial strains (S. aureus, E. coli, A. hydrophila and Vibrio) were selected as microfoulants for a laboratory antibacterial and biofilm susceptibility assay investigation. Our outcomes unveiled a novel promising ecofriendly biocidal agent with excellent and broad antibacterial efficacy compared to parent chitosan and the standard antifoulant, Diuron®. The fabricated poly-IL-brushes chitosan architectures were subjected to a rigorous test in a field trial in Red Sea water. Our findings provide new insights into eco-friendly antifouling additives as an alternative to traditional antifouling agents. Novel IL-functionalized chitosan-based coatings exhibited long-term durability, surface inertness and promising antifouling performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...