Glucose-assisted transformation of Ni-doped-ZnO@carbon to a Ni-doped-ZnO@void@SiO2 core–shell nanocomposite photocatalyst†
Abstract
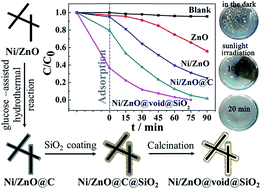
Carbon-coated nickel-doped-ZnO nanorods (Ni/ZnO@C NRs) are successfully prepared for the purpose of improving the visible-light photocatalytic performance of ZnO by expanding the absorption in the visible-light region and increasing the separation efficiency of photogenerated charges. The physicochemical properties of the catalysts were characterized using SEM, TEM, XRD, and Raman, FT-IR, UV-vis diffuse reflectance and PL spectra. The results indicated that nickel ions substituted for Zn2+ in the lattice of ZnO, whereas all the carbon was uniformly coated on the surface of the nanorod photocatalysts. Among the Ni/ZnO@C samples with different ion-doping levels and carbon coating content, the 1.0 mol% Ni/ZnO@C-3 sample possessing a carbon layer thickness of 3.8 nm exhibited a higher visible light activity and synergistic effects of the nickel and carbon, which were responsible for improving the photocatalytic activity. By using the hydrothermal carbon layer as a sacrificial template, nanovoid core–shell structured Ni/ZnO@void@SiO2 was obtained through subsequent silica coating and calcination reactions. Its porous shell could adsorb dye molecules from the bulk solution and accumulate them in the void space where the Ni/ZnO core is more accessible than for the bare Ni/ZnO nanorods in bulk solution, meanwhile the nanovoid structure could also avoid shielding of the catalyst-active sites by the outer layer, which leads to a significant photocatalytic activity enhancement. In addition, antibacterial studies of Ni/ZnO@void@SiO2 under sunlight irradiation were performed against Escherichia coli. This nanovoid photocatalyst exhibited high inhibition of the Gram-negative bacterial strain with co-action of the surface adsorption of the mesoporous SiO2 and the strong oxidation abilities of the formed reactive oxygen species.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...