Au(i) N-heterocyclic carbenes from bis-imidazolium amphiphiles: synthesis, cytotoxicity and incorporation onto gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
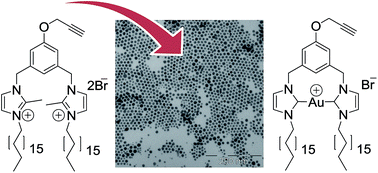
A gold(I) N-heterocyclic carbene 4 from a bis-imidazolium-amphiphile was synthesized and characterized. The cytotoxicity against HT-29 colon carcinoma and MDA-MB-231 breast adenocarcinoma cells was assessed for the NHC complex 4, the imidazolium salt precursor 2, and its methyl analogue 3, indicating that compounds 2–4 are promising cytotoxic agents. Furthermore, the ability of these compounds to be associated with gold nanoparticles was also explored, in order to develop an anticancer drug delivery system. The free ligands displayed more activity when compared with the ligands immobilized on the gold nanoparticles. The synthesized gold particles incorporating the bis-imidazolium salts either 2 or 3 showed monodisperse spherical shape with sizes of approximately 5 nm.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...