Redox controlled reversible transformation of a supramolecular alternating copolymer to a radical cation containing homo-polymer†
Abstract
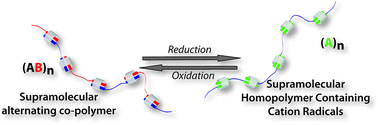
Research in the area of supramolecular polymeric materials has grown substantially in recent years owing to their potential applications in drug delivery, sensing, and catalysis. In this work, a supramolecular polymer has been prepared using the hetero-ternary complexation of cucurbit[8]uril (CB[8]). The CB[8] mediated ternary complexation of a viologen dimer and a tryptophan dimer led to the formation of a supramolecular alternating copolymer of (AB)n type. The polymer was characterized using UV-visible, fluorescence, 1H and DOSY NMR, DLS, and microscopy techniques. The copolymer led to the formation of well dispersed micro-globules of average diameter between 150 and 250 nm. Upon reduction of the viologen units of the copolymer, viologen radical cations were formed in the solution. These viologen radical cations displaced the second guest (tryptophan units) and formed dimers inside the CB[8] cavity. This complexation by viologen radical cations eventually led to the formation of a homo-polymer of (A)n type. The degree of polymerization was calculated to be approximately three times that of the copolymer, and larger micro-globules (∼950 nm) were obtained. Upon oxidation of the homo-polymer, the system reverted to the original co-polymer system. The reversible transformation can be achieved several times by controlling the redox reaction. A similar homo-polymer was also obtained by reducing the viologen dimer in the presence of CB[8].

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...