Matrix metalloproteinase-based photodynamic molecular beacons for targeted destruction of bone metastases in vivo†
Abstract
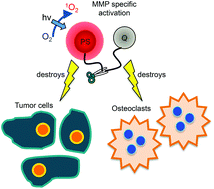
The metastatic spread of cancer from the primary site or organ is one of its most devastating aspects, being responsible for up to 90% of cancer-associated mortality. Bone is one of the common sites of metastatic spread, including the vertebrae. Regardless of the treatment strategy, the clinical goals for patients with vertebral metastases are to improve the quality of life by preventing neurologic decline, to achieve durable pain relief and enhance local tumor control. However, in part due to the close proximity of the spinal cord, current treatment options are limited. We propose a novel therapeutic strategy with the use of photodynamic molecular beacons (PMBs) for targeted destruction of spinal metastases, particularly to de-bulk lesions as an adjuvant to vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty in order to mechanically stabilize weak or fractured vertebrae. The PDT efficacy of a matrix metalloproteinase-specific PMB is reported in a metstatic model that recapitulates the clinical features of tumor growth within the bone. We demonstrate that not only does tumor cell destruction occur but also the killing of bone stromal cells. The potential of PMB-PDT to destroy metastatic tumors, disrupt the osteolytic cycle and better preserve critical organs with an increased therapeutic window compared with conventional photosensitizers is demonstrated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...