Delivering aminopyridine ligands into cancer cells through conjugation to the cell-penetrating peptide BP16†
Abstract
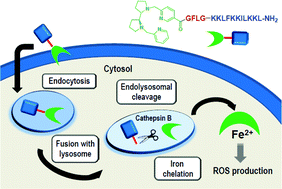
Peptide conjugates incorporating the N-based ligands Me2PyTACN or (S,S′)-BPBP at the N- or the C-terminus of the cell-penetrating peptide BP16 were synthesized (PyTACN–BP16 (BP341), BP16-PyTACN (BP342), BPBP–BP16 (BP343), and BP16-BPBP (BP344)). Metal binding peptides bearing at the N-terminus the ligand, an additional Lys and a β-Ala were also prepared (PyTACN-βAK–BP16 (BP345) and BPBP-βAK–BP16 (BP346)). Moreover, taking into account the clathrin-dependent endocytic mechanism of BP16, the enzymatic cleavable tetrapeptide Gly-Phe-Leu-Gly was incorporated between the ligand and the N- or C-terminus of BP16 (BPBP-GFLG-BP16 (BP347) and BP16-GLFG-BPBP (BP348)). Analysis of the cytotoxicity of all the peptide conjugates showed that: (i) the position of the ligand influenced the IC50 values, (ii) the incorporation of the βAla-Lys dipeptide rendered non active sequences, (iii) peptide conjugates derived from the (S,S′)-BPBP ligand were more active than those bearing Me2PyTACN, and (iv) the introduction of the cleavable tetrapeptide significantly enhanced the activity of the BPBP conjugates (IC50 of 4.3 to 11.7 μM (BP347 and BP348) compared to 26.0 to >50 μM (BP343, BP344 and BP346)). The most active peptide was BPBP-GFLG-BP16 (BP347) (IC50 of 4.3 to 5.0 μM). This high activity was attributed to its high internalization in MCF-7 cells, as shown by flow cytometry, and to the subsequent release of the ligand by the intracellular cleavage of the enzyme-labile spacer, as observed in cathepsin B enzymatic assays. Therefore, these results pave the way for the design of novel peptide conjugates to be used in pro-oxidant anticancer therapies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...