Lipophosphoramidate-based bipolar amphiphiles: their syntheses and transfection properties†
Abstract
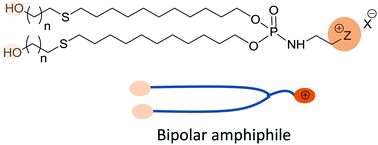
Six new cationic bolaamphiphiles (also called bipolar amphiphiles, bolaform amphiphiles, or bolalipids) were readily prepared by a thiol–ene click reaction that engaged a mercapto-alcohol (mercapto-ethanol or mercapto-hexanol) and a cationic based lipophosphoramidate. The cationic lipophosphoramidates contain two lipid chains that end in an alkene group and a selected cationic polar head group (trimethylammonium, dimethyl hydroxyethyl ammonium, or methylimidazolium). These compounds were formulated in water (with or without DOPE as a colipid) to produce supramolecular aggregates. These aggregates, before (i.e. bolasomes) and after (i.e. bolaplexes) mixing with plasmid DNA (pDNA) at various charge ratios, were characterized with regard to their sizes and zeta potentials. In the case of bolasomes, the suspensions were unstable since precipitation occurred after only a few hours at room temperature. On the other hand, bolaplex formulations exhibited clearly a better colloidal stability. Then, the gene delivery properties of the cationic bolasomes were investigated using two human-derived epithelial cell lines (A549 and 16HBE). Compared to the commercially available lipofection reagent (Lipofectamine), most of the cationic bolaamphiphiles were able to efficiently transfect these cells when they were formulated with DOPE in a 1 : 1 molar ratio. We report herein that bolaamphiphiles possessing a trimethylammonium or a dimethyl hydroxyethyl ammonium head group were the most efficient in terms of transfection efficiency while exhibiting no significant cytotoxicity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...