Palladium-catalyzed enolate arylation as a key C–C bond-forming reaction for the synthesis of isoquinolines†
Abstract
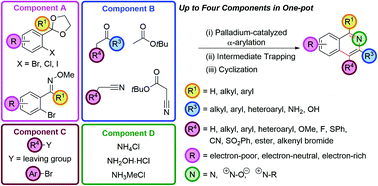
The palladium-catalyzed coupling of an enolate with an ortho-functionalized aryl halide (an α-arylation) furnishes a protected 1,5-dicarbonyl moiety that can be cyclized to an isoquinoline with a source of ammonia. This fully regioselective synthetic route tolerates a wide range of substituents, including those that give rise to the traditionally difficult to access electron-deficient isoquinoline skeletons. These two synthetic operations can be combined to give a three-component, one-pot isoquinoline synthesis. Alternatively, cyclization of the intermediates with hydroxylamine hydrochloride engenders direct access to isoquinoline N-oxides; and cyclization with methylamine, gives isoquinolinium salts. Significant diversity is available in the substituents at the C4 position in four-component, one-pot couplings, by either trapping the in situ intermediate after α-arylation with carbon or heteroatom-based electrophiles, or by performing an α,α-heterodiarylation to install aryl groups at this position. The α-arylation of nitrile and ester enolates gives access to 3-amino and 3-hydroxyisoquinolines and the α-arylation of tert-butyl cyanoacetate followed by electrophile trapping, decarboxylation and cyclization, C4-functionalized 3-aminoisoquinolines. An oxime directing group can be used to direct a C–H functionalization/bromination, which allows monofunctionalized rather than difunctionalized aryl precursors to be brought through this synthetic route.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...