Self-assembly of anionic, ligand-coated nanoparticles in lipid membranes†
Abstract
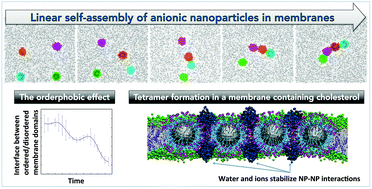
Ligand-functionalized nanoparticles (NPs) are a promising platform for imaging and drug delivery applications. A number of recent molecular simulation and theoretical studies explored how these NPs interact with model lipid membranes. However, interactions between ligand-coated NPs leading to possible cooperative effects and association have not been investigated. In this coarse-grained molecular dynamics study, we focus on a specific case of several anionic, ligand-coated NPs embedded in a lipid membrane. Several new effects are observed. Specifically, in the presence of cholesterol in the membrane, NPs tend to form linear clusters, or chains. Analysis of the driving forces for this association reveals an important role of the recently discovered orderphobic effect, although we acknowledge that a combination of factors must be at play. At the same time, we argue that the specific linear shape of the clusters is a result of a subtle balance between the forces that stabilize a NP in the membrane and the forces that drive the NP–NP association processes. These effects, observed for the first time in the NP-membrane systems, have also direct correspondence to similar effects in protein-membrane systems and these links between the two realms should be explored further.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...