Enlightening the ultrahigh electrical conductivities of doped double-wall carbon nanotube fibers by Raman spectroscopy and first-principles calculations†
Abstract
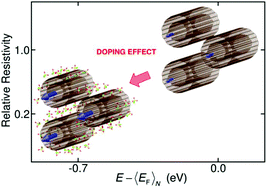
Highly aligned, packed, and doped carbon nanotube (CNT) fibers with electrical conductivities approaching that of copper have recently become available. These fibers are promising for high-power electrical applications that require light-weight, high current-carrying capacity cables. However, a microscopic understanding of how doping affects the electrical conductance of such CNT fibers in a quantitative manner has been lacking. Here, we performed Raman spectroscopy measurements combined with first-principles calculations to determine the position of the average Fermi energy and to obtain the temperature of chlorosulfonic-acid-doped double-wall CNT fibers under high current. Due to the unique way in which double-wall CNT Raman spectra depend on doping, it is possible to use Raman data to determine the doping level quantitatively. The correspondence between the Fermi level shift and the carbon charge transfer is derived from a tight-binding model and validated by several calculations. For the doped fiber, we were able to associate an average Fermi energy shift of ∼−0.7 eV with a conductance increase by a factor of ∼5. Furthermore, since current induces heating, local temperature determination is possible. Through the Stokes-to-anti-Stokes intensity ratio of the G-band peaks, we estimated a temperature rise at the fiber surface of ∼135 K at a current density of 2.27 × 108 A m−2 identical to that from the G-band shift, suggesting that thermalization between CNTs is well achieved.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...