Albumin-coated SPIONs: an experimental and theoretical evaluation of protein conformation, binding affinity and competition with serum proteins†
Abstract
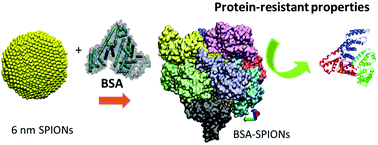
The variety of nanoparticles (NPs) used in biological applications is increasing and the study of their interaction with biological media is becoming more important. Proteins are commonly the first biomolecules that NPs encounter when they interact with biological systems either in vitro or in vivo. Among NPs, super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) show great promise for medicine. In this work, we study in detail the formation, composition, and structure of a monolayer of bovine serum albumin (BSA) on SPIONs. We determine, both by molecular simulations and experimentally, that ten molecules of BSA form a monolayer around the outside of the SPIONs and their binding strength to the SPIONs is about 3.5 × 10−4 M, ten times higher than the adsorption of fetal bovine serum (FBS) on the same SPIONs. We elucidate a strong electrostatic interaction between BSA and the SPIONs, although the secondary structure of the protein is not affected. We present data that supports the strong binding of the BSA monolayer on SPIONs and the properties of the BSA layer as a protein-resistant coating. We believe that a complete understanding of the behavior and morphology of BSA-SPIONs and how the protein interacts with SPIONs is crucial for improving NP surface design and expanding the potential applications of SPIONs in nanomedicine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...