Genetically designed biomolecular capping system for mesoporous silica nanoparticles enables receptor-mediated cell uptake and controlled drug release†
Abstract
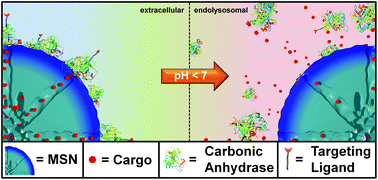
Effective and controlled drug delivery systems with on-demand release and targeting abilities have received enormous attention for biomedical applications. Here, we describe a novel enzyme-based cap system for mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) that is directly combined with a targeting ligand via bio-orthogonal click chemistry. The capping system is based on the pH-responsive binding of an aryl-sulfonamide-functionalized MSN and the enzyme carbonic anhydrase (CA). An unnatural amino acid (UAA) containing a norbornene moiety was genetically incorporated into CA. This UAA allowed for the site-specific bio-orthogonal attachment of even very sensitive targeting ligands such as folic acid and anandamide. This leads to specific receptor-mediated cell and stem cell uptake. We demonstrate the successful delivery and release of the chemotherapeutic agent Actinomycin D to KB cells. This novel nanocarrier concept provides a promising platform for the development of precisely controllable and highly modular theranostic systems.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating the 2017 RSC Prize and Award Winners

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...