Surface reactivity of non-hydrolytic silicophosphate xerogels: a simple method to create Brønsted or Lewis acid sites on porous supports†
Abstract
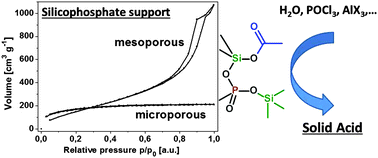
Non-hydrolytic sol–gel reactions of silicon acetates with trimethylsilyl (TMS) esters of phosphoric and phosphonic acids produce cross-linked matrices containing homogeneous dispersions of silicate and phosphoryl groups connected together by networks of Si–O–P(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) linkages. The condensation degrees reach 80 to 90%. Residual organic groups (10 to 20%) were reacted with a variety of compounds (H2O, Me3SiOSiMe3, POCl3, SiCl4, AlMe3, Al(NMe2)3, and AlCl3) in order to enrich the surface of these porous matrices with Brønsted (
O) linkages. The condensation degrees reach 80 to 90%. Residual organic groups (10 to 20%) were reacted with a variety of compounds (H2O, Me3SiOSiMe3, POCl3, SiCl4, AlMe3, Al(NMe2)3, and AlCl3) in order to enrich the surface of these porous matrices with Brønsted (![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) P–OH) and Lewis (tetracoordinated Al) acid functional groups. The differences in the reactivity of
P–OH) and Lewis (tetracoordinated Al) acid functional groups. The differences in the reactivity of ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) Si–OAc and
Si–OAc and ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) P–OSiMe3 groups were utilized for the selective modification at the silicon and phosphorus atoms. The reaction procedures were optimized and significantly porous silicophosphate materials with a high content of either hydroxyl groups or four-coordinated aluminium species were obtained. The activity and selectivity of prepared samples as catalysts for the dimerization of α-methylstyrene were tested. Excellent activities and moderate to very high selectivities were achieved suggesting the potential use of silicophosphate xerogels in heterogeneous catalysis.
P–OSiMe3 groups were utilized for the selective modification at the silicon and phosphorus atoms. The reaction procedures were optimized and significantly porous silicophosphate materials with a high content of either hydroxyl groups or four-coordinated aluminium species were obtained. The activity and selectivity of prepared samples as catalysts for the dimerization of α-methylstyrene were tested. Excellent activities and moderate to very high selectivities were achieved suggesting the potential use of silicophosphate xerogels in heterogeneous catalysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...