Design of simvastatin-loaded polymeric microbubbles as targeted ultrasound contrast agents for vascular imaging and drug delivery in the identification of atherosclerotic plaque
Abstract
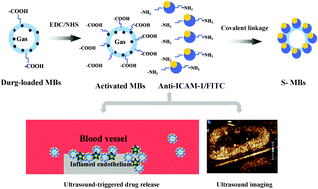
Targeting ultrasound contrast agents (UCAs) offer further opportunity to enhance the capabilities of diagnostic ultrasound imaging and controlled drug delivery to pathological tissue. In this study, simvastatin (Sim) loaded polymeric microbubbles (MBs) as UCAs were developed and targeted toward inflamed vascular endothelium to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis. The polymeric shelled MBs were used to enable localized targeting of the inflamed vascular endothelium by modifying the surface of these MBs with specific antibodies. The morphology, size distribution, chemical composition and antibody conjugation efficiency of the MBs were evaluated. The gas-filled drug delivery platform described promises faster drug release, when subjected to ultrasound, compared to the drug release without ultrasound. In vivo ultrasound contrast imaging confirmed that these polymeric MBs could provide a stable acoustic enhancement and effectively identify atherosclerotic areas of plaque within the ventral aorta of rabbits. The results demonstrated that the elaboration of MBs has the potential to exhibit excellent ultrasound contrast-enhancing capabilities and provide a sufficient amount of drug to target disease sites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...