Identification of Gli-mediated transcription inhibitors through synthesis and evaluation of taepeenin D analogues†‡
Abstract
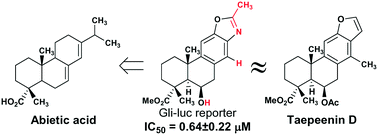
The Hedgehog pathway has emerged as a favourable target to address drug resistance in cancer stem cells. Inhibitors of Gli1, the terminal effector of the pathway, are anticipated to evade drug resistance and to display fewer side effects than inhibitors targeting Smo. Inspired by the Gli-mediated transcription inhibitor taepeenin D, synthesis and evaluation of a series of second generation analogues has led to the enrichment of available structure–activity relationships for this natural product and has identified an oxazole analogue as an improved lead compound.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...