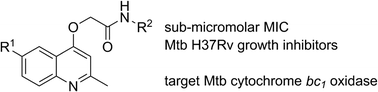
SAR and identification of 2-(quinolin-4-yloxy)acetamides as Mycobacterium tuberculosis cytochrome bc1 inhibitors†‡
Abstract
A previous phenotypic screen by GSK identified 2-(quinolin-4-yloxy)acetamides as potent growth inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). We report the results of a preliminary structure–activity relationship (SAR) study of the compound class which has yielded more potent inhibitors. An Mtb cytochrome bd oxidase deletion mutant (cydKO) was found to be hypersensitive to most members of the compound library, while strains carrying single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the qcrB gene, which encodes a subunit of the menaquinol cytochrome c oxidoreductase (bc1) complex, were resistant to the library. These results identify that the 2-(quinolin-4-yloxy)acetamide class of Mtb growth inhibitors can be added to the growing number of scaffolds that target the M. tuberculosis bc1 complex.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...