The proteome of methylmalonic acidemia (MMA): the elucidation of altered pathways in patient livers†
Abstract
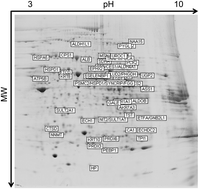
Methylmalonic acidemia (MMA) is a heterogeneous and severe autosomal recessive inborn error of metabolism most commonly caused by the deficient activity of the vitamin B12 dependent enzyme, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MUT). The main treatment for MMA patients is the dietary restriction of propiogenic amino acids and carnitine supplementation. Despite treatment, the prognosis for vitamin B12 non-responsive patients remains poor and is associated with neonatal lethality, persistent morbidity and decreased life expectancy. While multi-organ pathology is a feature of MMA, the liver is severely impacted by mitochondrial dysfunction which likely underlies the metabolic instability experienced by the patients. Liver and/or combined liver/kidney transplantation is therefore sometimes performed in severely affected patients. Using liver specimens from donors and MMA patients undergoing elective liver transplantation collected under a dedicated natural history protocol (clinicaltrials.gov: NCT00078078), we employed proteomics to characterize the liver pathology and impaired hepatic metabolism observed in the patients. Pathway analysis revealed perturbations of enzymes involved in energy metabolism, gluconeogenesis and Krebs cycle anaplerosis. Our findings identify new pathophysiologic and therapeutic targets that could be valuable for designing alternative therapies to alleviate clinical manifestations seen in this disorder.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...