Spectroscopic characterization of a low-temperature plasma ambient ionization probe operated with helium/nitrogen plasma gas mixtures
Abstract
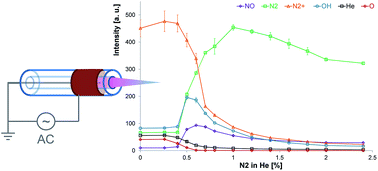
In this study, a systematic spectroscopic characterization of a low-temperature plasma (LTP) probe operated with He/N2 gas mixtures is carried out. The influence of several experimental parameters (e.g., different He/N2 gas mixtures, discharge voltage, and gas flow rate) on the dielectric-barrier discharge afterglow was studied. It was found that an increase of the nitrogen concentration in the helium discharge gas (to values higher than 0.5% N2) leads to a significant decay of N2+, He, and O emission intensities. At 1% N2 and 99% He, oxygen emission bands were not detectable and intensity of He and N2+ emission bands were reduced by approximately five times compared to features in a 100% He discharge. Interestingly, the opposite trend was observed for NO, OH, and N2 species. Here, increasing the N2 fraction in the discharge gas mixture led to an enhancement of emission intensities. Maximum emission bands intensities of OH, NO, and N2 were detected at N2 concentrations of 0.5, 0.6, and 1.0%, respectively. A further increase of the N2 fraction leads to a decrease of emission intensities for all observed species (OH, NO, N2, He, and N2+). In general, an increase in discharge gas flow rate resulted in a significant increase of NO emission band intensities for all N2/He mixtures tested. However, only a minor effect was observed for N2 emission bands. Increasing the discharge voltage resulted in an increase of emission intensities of all detected species. Combined with spatially resolved investigations of the afterglow, these results are considered helpful to further optimize LTP performance. This is especially important for portable and direct analysis instrumentation, where LTP can be used as the ionization source and lower helium gas consumption is desirable because of cost and availability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...