Vitamin C boosts ceria-based catalyst recycling†
Abstract
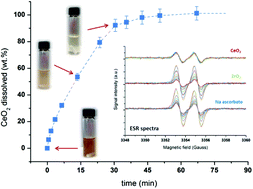
The facile, rapid, and complete reductive dissolution of CeO2 and ceria-based oxides, known to be highly refractive materials towards dissolution, is reported for the first time in very mild conditions. Ceria samples are dissolved at room temperature under stirring in a mixture composed of ascorbic acid and a dilute mineral acid. Normalized dissolution kinetics are compared as a function of the concentration of reactants, nature of the mineral acid, firing temperature and reactive surface area of considered oxides. Since ceria dissolution can represent a promising alternative for the recycling of automotive catalysts, solid oxide fuel cells, polishing powders, organic chemistry catalysts, sensors, etc., the potential application of the proposed procedure is then studied through the dissolution of catalyst surrogates and complex oxides: Pt/CeO2, (Ce0.75Zr0.25)O2, and (Ce0.8Tb0.2)O2. Whatever the considered sample, the complete and congruent (for mixed oxides) oxide dissolution is observed in 0.5 M ascorbic acid in the presence of dilute nitric or sulfuric acid. For Pt/CeO2 samples, ceria dissolution goes with Pt aggregation which can be easily recovered from the solution after processing due to its high stability in this medium. This eco-friendly and efficient method appears very promising for catalyst recycling in comparison to conventional procedures. After rigorous characterization of the investigated oxides (BET, SEM-EDX, XRD, TGA), dissolution progress is evaluated with ICP-OES and SEM measurements. The dissolution mechanism is then investigated with UV-Vis, ATR-FTIR and ESR spectroscopies and a general dissolution mechanism is proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...