Antioxidant activity in vitro and in vivo of the polysaccharides from different varieties of Auricularia auricula
Abstract
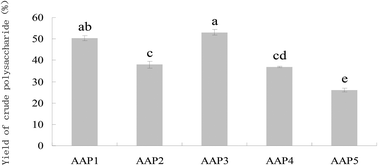
In this study, five different kinds of polysaccharides (AAP1, AAP2, AAP3, AAP4, and AAP5) were extracted from different varieties of Auricularia auricula through an alkali extraction process. Furthermore, the crude polysaccharides were deproteinized by the Sevag method. Auricularia auricula produced in the Shanxi province had the highest content of polysaccharide, 53.02%. The monosaccharide composition was determined by the GC method. Their antioxidant capacities in vitro were assessed by radical-scavenging capacity (DPPH, superoxide, and hydroxyl radicals), metal chelating ability and reducing-power methods. In addition, the evaluation of their antioxidant effects in vivo was performed using the C. elegans model. The yield of crude polysaccharides, monosaccharide composition and antioxidant activity of Auricularia auricula polysaccharides (AAPs) were different among samples from various sources. Among them, the strongest antioxidant activity was shown for AAP1, consisting of arabinose, xylose, 2-deoxy-D-glucose, mannose, glucose, and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine with the molar ratio of 1 : 0.44 : 0.33 : 1.67 : 1 : 0.17. It could scavenge free radicals, up-regulate stress-resistance-related enzymes including superoxide dismutase (SOD) by 70.04 ± 8.75% and CAT by 117.32 ± 8.06% and reduce the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in C. elegans under oxidative stress. The present results suggested that variety was an important factor that affects the antioxidant activity of A. auricula polysaccharides.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...