Physical and oxidative stability of functional olive oil-in-water emulsions formulated using olive mill wastewater biophenols and whey proteins
Abstract
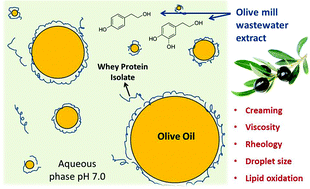
The present paper reports on the use of phenolic extracts from olive mill wastewater (OMW) in model olive oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions to study their effect on their physical and chemical stability. Spray-dried OMW polyphenols were added to a model 20% olive O/W emulsion stabilized with whey protein isolate (WPI) and xanthan gum, in phosphate buffer solution at pH 7. The emulsions were characterised under accelerated storage conditions (40 °C) up to 30 days. Physical stability was evaluated by analysing the creaming rate, mean particle size distribution and mean droplet size, viscosity and rheological properties, while chemical stability was assessed through the measurement of primary and secondary oxidation products. The rheological behaviour and creaming stability of the emulsions were dramatically improved by using xanthan gum, whereas the concentration of WPI and the addition of encapsulated OMW phenolics did not result in a significant improvement of physical stability. The formation of oxidation products was higher when higher concentrations of encapsulated polyphenols were used, indicating a possible binding with the WPI added in the system as a natural emulsifier. This paper might help in solving the issue of using the olive mill wastewater from olive processing in formulating functional food products with high antioxidant activity and improved health properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...