Exceptional energy and new insight with a sodium–selenium battery based on a carbon nanosheet cathode and a pseudographite anode†
Abstract
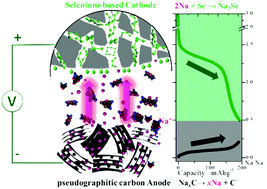
We created a unique sodium ion battery (NIB, SIB) cathode based on selenium in cellulose-derived carbon nanosheets (CCNs), termed Se-CCN. The elastically compliant two-dimensional CCN host incorporates a high mass loading of amorphous Se (53 wt%), which is primarily impregnated into 1 cm3 g−1 nanopores. The results in facile sodiation kinetics due to short solid-state diffusion distances and a large charge transfer area of the nanosheets were established. The architecture also leads to an intrinsic resistance to polyselenide shuttle and to disintegration/coarsening. As a Na half-cell, the Se-CCN cathode delivers a reversible capacity of 613 mA h g−1 with 88% retention over 500 cycles. The exceptional stability is achieved by using a standard electrolyte (1 M NaClO4 EC-DMC) without secondary additives or high salt concentrations. The rate capability is also superb, achieving 300 mA h g−1 at 10C. Compared to recent state-of-the-art literature, the Se-CCN is the most cyclically stable and offers the highest rate performance. As a Se–Na battery, the system achieves 992 W h kg−1 at 68 W kg−1 and 384 W h kg−1 at 10 144 W kg−1 (by active mass in a cathode). We are the first to fabricate and test a Se-based full NIB, which is based on Se-CCN coupled to a Na intercalating pseudographitic carbon (PGC) anode. It is demonstrated that the PGC anode increases its structural order in addition to dilating as a result of Na intercalation at voltages below 0.2 V vs. Na/Na+. The {110} Na reflections are distinctly absent from the XRD patterns of PGC sodiated down to 0.001 V, indicating that the Na metal pore filling is not significant for pseudographitic carbons. The battery delivers highly promising Ragone chart characteristics, for example yielding 203 and 50 W h kg−1 at 70 and 14 000 W kg−1 (via total material mass in the anode and cathode).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...