Systematic molecular engineering of Zn-ketoiminates for application as precursors in atomic layer depositions of zinc oxide†
Abstract
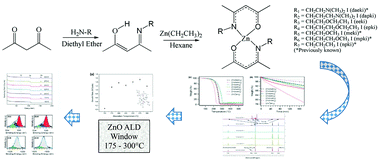
Molecular engineering of seven closely related zinc ketoiminates, namely, [Zn(dapki)2], [Zn(daeki)2], [Zn(epki)2], [Zn(eeki)2], [Zn(mpki)2], [Zn(meki)2], and [Zn(npki)2], leads to the optimisation of precursor thermal properties in terms of volatilisation rate, onset of volatilisation, reactivity and thermal stability. The influence of functional groups at the imine side chain of the ligands on the precursor properties is studied with regard to their viability as precursors for atomic layer deposition (ALD) of ZnO. The synthesis of [Zn(eeki)2], [Zn(epki)2] and [Zn(dapki)2] and the crystal structures of [Zn(mpki)2], [Zn(eeki)2], [Zn(dapki)2] and [Zn(npki)2] are presented. From the investigation of the physico-chemical characteristics, it was inferred that all compounds are monomeric, volatile and exhibit high thermal stability, all of which make them promising ALD precursors. Compound [Zn(eeki)2] is in terms of thermal properties the most promising Zn-ketoiminate. It is reactive towards water, possesses a melting point of 39 °C, is stable up to 24 days at 220 °C and has an extended volatilisation rate compared to the literature known Zn-ketoiminates. It demonstrated self-saturated, water assisted growth of zinc oxide (ZnO) with growth rates in the order of 1.3 Å per cycle. Moreover, it displayed a broad temperature window from TDep = 175–300 °C and is the first report of a stable high temperature (>200 °C) ALD process for ZnO returning highly promising growth rates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...