Pyridylphosphinate metal complexes: synthesis, structural characterisation and biological activity†
Abstract
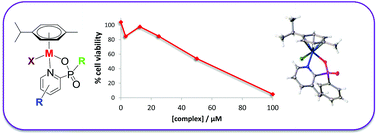
For the first time, a series of 25 pseudo-octahedral pyridylphosphinate metal complexes (Ru, Os, Rh, Ir) has been synthesised and assessed in biological systems. Each metal complex incorporates a pyridylphosphinate ligand, a monodentate halide and a capping η6-bound aromatic ligand. Solid- and solution-state analyses of two complexes reveal a structural preference for one of a possible two diastereomers. The metal chlorides hydrolyse rapidly in D2O to form a 1 : 1 equilibrium ratio between the aqua and chloride adducts. The pKa of the aqua adduct depends upon the pyridyl substituent and the metal but has little dependence upon the phosphinate R′ group. Toxicity was measured in vitro against non-small cell lung carcinoma H460 cells, with the most potent complexes reporting IC50 values around 50 μM. Binding studies with selected amino acids and nucleobases provide a rationale for the variation in toxicity observed within the series. Finally, an investigation into the ability of the chelating amino acid L-His to displace the phosphinate O–metal bond shows the potential for phosphinate complexes to act as prodrugs that can be activated in the intracellular environment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...