Probing the interaction of U(vi) with phosphonate-functionalized mesoporous silica using solid-state NMR spectroscopy†
Abstract
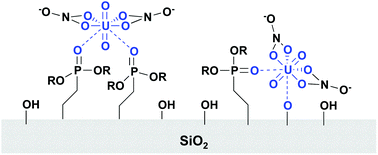
The fundamental interaction of U(VI) with diethylphosphatoethyl triethoxysilane functionalized SBA-15 mesoporous silica is studied by macroscopic batch experiments and solid-state NMR spectroscopy. DPTS-functionalized silica has been shown to extract U(VI) from nitric acid solutions at or above pH 3. Extraction is dependent on pH and ionic strength. Single-pulse 31P NMR on U(VI) contacted samples revealed that U(VI) only interacts with a fraction of the ligands present on the surface. At pH 4 the U(VI) extraction capacity of the material is limited to 27–37% of the theoretical capacity, based on ligand loading. We combined single pulse 31P NMR on U(VI)-contacted samples with batch studies to measure a ligand-to-metal ratio of approximately 2 : 1 at pH 3 and 4. Batch studies and cross-polarization NMR measurements reveal that U(VI) binds to deprotonated phosphonate and/or silanol sites. We use 31P–31P DQ-DRENAR NMR studies to compare the average dipolar coupling between phosphorus spins for both U(VI)-complexed and non-complexed ligand environments. These measurements reveal that U(VI) extraction is not limited by inadequate surface distribution of ligands, but rather by low stability of the surface phosphonate complex.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...