Significantly enhanced proteolytic activity of cyclen complexes by monoalkylation†
Abstract
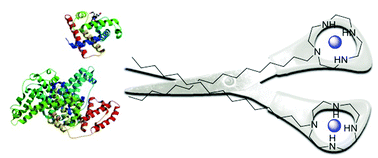
A simple approach towards efficient artificial proteases based on the cyclen ligand is presented. We thus achieved an increase of the proteolytic activity of two orders of magnitude when compared to the unsubstituted cyclen complex. Amphiphilic Cu(II) and Co(III) complexes cut BSA and myoglobin as model substrates at μM concentrations. MALDI-ToF MS is used to identify the cleavage fragments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...