Mechanisms and reactivity differences of proline-mediated catalysis in water and organic solvents
Abstract
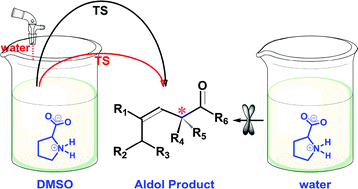
Proline is an efficient and versatile catalyst for organic reactions while a number of issues remain controversial. Here, ab initio and density functional calculations were used to unravel a few key issues of catalytic mechanisms in water and organic solvents. Zwitterionic proline that predominates in water and DMSO is assumed to be the active conformation for catalysis, and reactivity differences in two solvents are revealed. Meanwhile, an abundance of experimental observations can be finely interpreted by the present computational results, including those seemingly contradictory. Although bearing lower activation barriers than that in DMSO, the production of enamines and further aldol products in water will be blocked at an early stage (J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 734) because the reaction in water is significantly driven towards acetyl formation that is kinetically and thermodynamically preferred. Due to significant promotion of the rate-determining proton transfer step, aldol reactions in organic solvents can be obviously initiated by the addition of some water (Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2004, 43, 1983). In order to show catalytic effects in water (an obviously environmentally benign solvent), proline has to be structurally modified so that canonical structures can be the principal (or sole) conformations, which is in line with the analyses of all proline-based catalysts available in water (e.g., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 734, Catal. Commun., 2012, 26, 6). Thus, the present results provide insightful clues to mechanisms of proline-mediated catalysis as well as future design of more efficient catalysts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...