Hydroxyl radical generation by cactus-like copper oxide nanoporous carbon catalysts for microcystin-LR environmental remediation†‡
Abstract
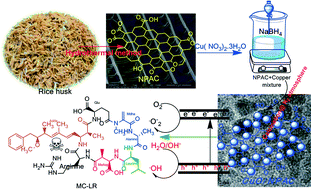
Copper oxide supported on nanoporous activated carbon (CuO-NPAC) is reported for the aqueous phase catalytic degradation of cyanotoxin microcystin-LR (MC-LR). The loading and spatial distribution of CuO throughout the NPAC matrix strongly influence the catalytic efficiency. CuO-NPAC synthesis was optimized with respect to the copper loading and thermal processing, and the physicochemical properties of the resulting materials were characterized by XRD, BET, TEM, SEM, EPR, TGA, XPS and FT-IR spectroscopy. EPR spin trapping and fluorescence spectroscopy showed in situ ˙OH formation via H2O2 over CuO-NPAC as the catalytically relevant oxidant. The impact of reaction conditions, notably CuO-NPAC loading, H2O2 concentration and solution pH, is discussed in relation to the reaction kinetics for MC-LR remediation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...