Capturing Cd(ii) and Pb(ii) from contaminated water sources by electro-deposition on hydrotalcite-like compounds†
Abstract
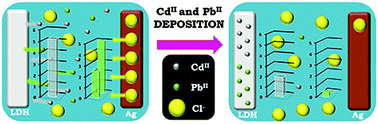
Two different hydrotalcite-like compounds were prepared and used as substrates for the electrochemical removal of extremely toxic pollutant cations, such as Cd(II) and Pb(II), from aqueous solutions, and their subsequent recovery for further potential applications. By deposition on the hydrotalcite electrode, it was possible to remove 75% of Cd(II) contained in a starting 5.2 mM solution of CdCl2, which was subsequently recovered and concentrated up to 14.3 mM in a single step. A removal of almost 100% was obtained in the case of Pb(II). Its recovery was largely hindered by the formation of several inert phases, among which is some stable formation of hydroxycarbonate. Our results suggest that the removal of these contaminants by hydrotalcite-like compounds occurs by the combination of two parallel processes: electro-deposition and adsorption. It was possible to achieve a removal capacity for Cd(II) and Pb(II) equal to 763 mg ga.m.−1 and 1039 mg ga.m.−1, respectively. These removal capacities, accompanied by an excellent posterior eluent-free recovery of Cd(II), suggest that this new method could be an environmentally friendly alternative to the conventional adsorption wastewater treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...