Convective heat transfer in a measurement cell for scanning electrochemical microscopy
Abstract
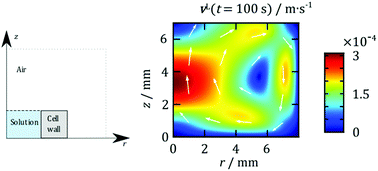
Electrochemical experiments, especially those performed with scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM), are often carried out without taking special care to thermostat the solution; it is usually assumed that its temperature is homogeneous and equal to the ambient. The present study aims to test this assumption via numerical simulations of the heat transfer in a particular system – the typical measurement cell for SECM. It is assumed that the temperature of the solution is initially homogeneous but different from that of its surroundings; convective heat transfer in the solution and the surrounding air is taken into account within the framework of the Boussinesq approximation. The hereby presented theoretical treatment indicates that an initial temperature difference of the order of 1 K dissipates with a characteristic time scale of ∼1000 s; the thermal equilibration is accompanied by convective flows with a maximum velocity of ∼10−4 m s−1; furthermore, the temporal evolution of the temperature profile is influenced by the sign of the initial difference. These results suggest that, unless the temperature of the solution is rigorously controlled, convection may significantly compromise the interpretation of data from SECM and other electrochemical techniques, which is usually done on the basis of diffusion-only models.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...