Adsorption of single 1,8-octanedithiol molecules on Cu(100)
Abstract
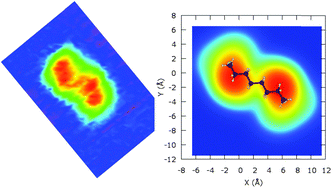
Single 1,8-octanedithiol (ODT) molecules adsorbed onto the Cu(100) surface have been characterized by using scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) and studied by semi-empirical calculations. STM images have revealed two types of chiral molecules on the surface upon adsorption and both types of molecules showed two bright spots at the extremities of a small rod due to the enhanced electronic density contrast of the chemisorbed sulfur atoms. In sub-monolayer regime deposition, ODT molecules exhibit preferential adsorption directions and the relaxation mechanism is driven by the chemisorption of the two sulfur atoms in a hollow site of the surface. By means of calculations several conformations of the molecule according to the energetically favorable alkane body stretching constraint have been studied. The comparison between relaxed conformations and between calculated and experimental STM images, followed by an analysis of different orientations, has allowed determining unambiguously the most favorable position of the ODT molecule on Cu(100).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...