Exciton coupling dynamics in syn- and anti-type β–β linked Zn(ii) porphyrin linear arrays†
Abstract
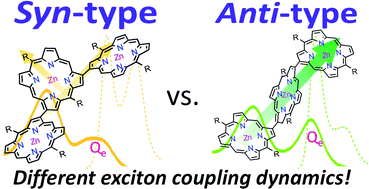
The photophysical properties of molecular arrays are strongly dependent on a variety of structural factors: the constituent chromophores, dihedral angle, linkage length, linkage position, the center-to-center distance between chromophores, and the linker itself. Here, we investigated the exciton coupling dynamics of syn- and anti-type β–β directly linked Zn(II) porphyrin linear arrays. Focusing on the relationship between the origin of the lowest excited electronic state and the linkage position, we evaluated the exciton coupling strength and carried out time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) calculations on model compounds as well as femtosecond transient absorption anisotropy (fs-TAA) measurements. Based on our experiments and calculations, we propose that a different origin of the lowest excited state leads to linkage-position-dependent exciton coupling. In short, compared with syn-type porphyrin arrays, anti-type arrays induce distinct and stronger exciton coupling in the lowest excited state.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...