Cation–cation and anion–anion complexes stabilized by halogen bonds†
Abstract
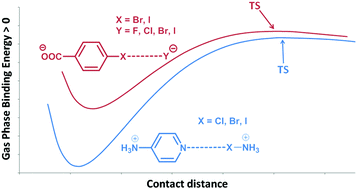
Stable minima showing halogen bonds between charged molecules with the same sign have been explored by means of theoretical calculations. The dissociation transition states and their corresponding barriers have also been characterized. In all cases, the results indicate that the complexes are thermodynamically unstable but kinetically stable with respect to the isolated monomers in gas phase. A corrected binding energy profile by removing the charge–charge repulsion of the monomers shows a profile similar to the one observed for the dissociation of analogous neutral systems. The nature of the interaction in the minima and TSs has been analyzed using the symmetry adapted perturbation theory (SAPT) method. The results indicate the presence of local favorable electrostatic interactions in the minima that vanish in the TSs. Natural bond orbital (NBO) and “atoms-in-molecules” (AIM) theories were used to analyze the complexes, obtaining good correlations between Laplacian and electron density values with both bond distances and charge-transfer energy contributions E(2). The largest E(2) orbital interaction energies for cation–cation and anion–anion complexes are 561.2 and 197.9 kJ mol−1, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...