Characterizing a nonclassical carbene with coupled cluster methods: cyclobutylidene†
Abstract
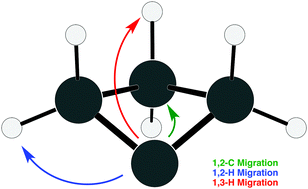
Carbenes represent a special class of reactive compounds that possess a lone pair of electrons on a carbon atom. Among the myriad examples of carbenes in the literature, cyclobutylidene stands out as a unique nonclassical compound that includes transannular interaction between opposing C1 and C3 carbon atoms within a four-membered ring. On its lowest potential energy surface (![[X with combining tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0058_0303.gif) 1A′), cyclobutylidene quickly rearranges, following three reaction paths: (i) 1,2-H migration; (ii) 1,2-C migration; and, (iii) 1,3-H migration. Herein, this reactivity is examined with high-level coupled-cluster methods [up to CCSDT(Q)]. At this level of theory, combined with extrapolation techniques to obtain energies at the complete basis set (CBS) limit, the long-standing disparity between theoretical and experimental results is resolved. Specifically, cyclobutylidene is predicted to prefer 1,2-C migration rather than 1,2-H migration. Rate constants for the three reaction paths are obtained from canonical variational transition state theory (CVT) and yield reasonable agreement with existing experimental results. Further characterization of cyclobutylidene is also reported: the singlet–triplet gap (ΔES–T) is found to be −9.3 kcal mol−1 at the CCSDT(Q)/CBS level of theory, and anharmonic vibrational frequencies are determined with second-order vibrational perturbation theory (VPT2).
1A′), cyclobutylidene quickly rearranges, following three reaction paths: (i) 1,2-H migration; (ii) 1,2-C migration; and, (iii) 1,3-H migration. Herein, this reactivity is examined with high-level coupled-cluster methods [up to CCSDT(Q)]. At this level of theory, combined with extrapolation techniques to obtain energies at the complete basis set (CBS) limit, the long-standing disparity between theoretical and experimental results is resolved. Specifically, cyclobutylidene is predicted to prefer 1,2-C migration rather than 1,2-H migration. Rate constants for the three reaction paths are obtained from canonical variational transition state theory (CVT) and yield reasonable agreement with existing experimental results. Further characterization of cyclobutylidene is also reported: the singlet–triplet gap (ΔES–T) is found to be −9.3 kcal mol−1 at the CCSDT(Q)/CBS level of theory, and anharmonic vibrational frequencies are determined with second-order vibrational perturbation theory (VPT2).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...