The effects of n-type doping on lithium storage in TiO2
Abstract
In this report, we discuss the Li-storage performance of niobium-doped TiO2 nanostructures (Ti1−yNbyO2+δ), with a special focus on the effects of ionic/electronic charge carrier concentration (defect chemistry) on Li storage and transport properties. By Nb-doping, Li storage kinetics of titania electrode material is significantly improved mainly due to the increased electronic charge carrier concentration (n-type doping). However, it was found that there is a maximum beyond which further doping is rather detrimental to Li diffusion kinetics. Defect chemical analysis indicates that this limited doping effect is due to the trapping of free lithium ions by the critical electron–ion association reactions at room temperature such as 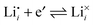 and
and 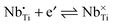 .
.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...