Association of defects in doped non-stoichiometric ceria from first principles
Abstract
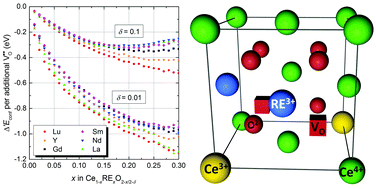
We investigate the interaction and distribution of defects in doped non-stoichometric ceria Ce1−xRExO2−x/2−δ (with RE = Lu, Y, Gd, Sm, Nd, and La) by combining DFT+U calculations and Monte Carlo simulations. The concentrated solution of defects in ceria is described by the pair interactions of dopant ions, oxygen vacancies, and small polarons. The calculated interaction energies for polarons and oxygen vacancies are in agreement with experimental results and previously reported calculations. Simulations reveal that in thermodynamic equilibrium the configurational energy decreases with increasing non-stoichiometry as well as increasing dopant fraction similar to the observed behavior of the enthalpy of reduction in experiments. This effect is attributed to the attractive interaction of oxygen vacancies with polarons and dopant ions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...